Phylum Cyanophyta (blue-green algae/cyanobacteria) - Search Algaevision
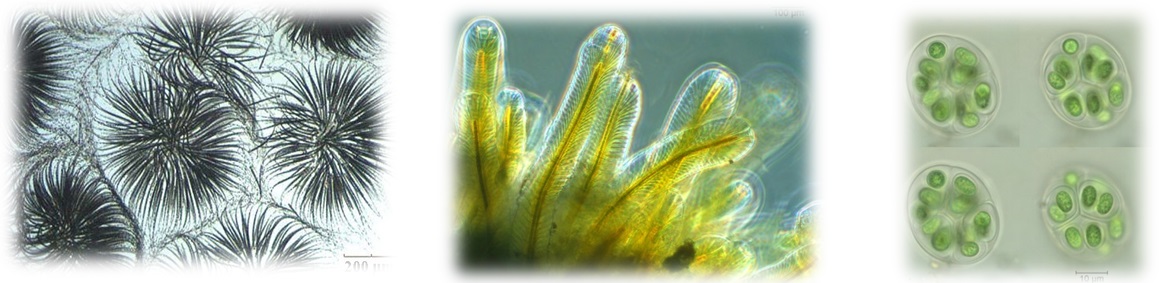
- blue-green, grey-green, violet, brown, purplish or red dependent on relative proportions of chlorophyll, phycocyanin and phycoerythrin
- sometimes a brown sheath pigment (scytonemin) present
- unicellular, colonial or filamentous (simple or branched)
- internal membranes absent and so no organelles
Phylum Rhodophyta (red algae) - Search Algaevision
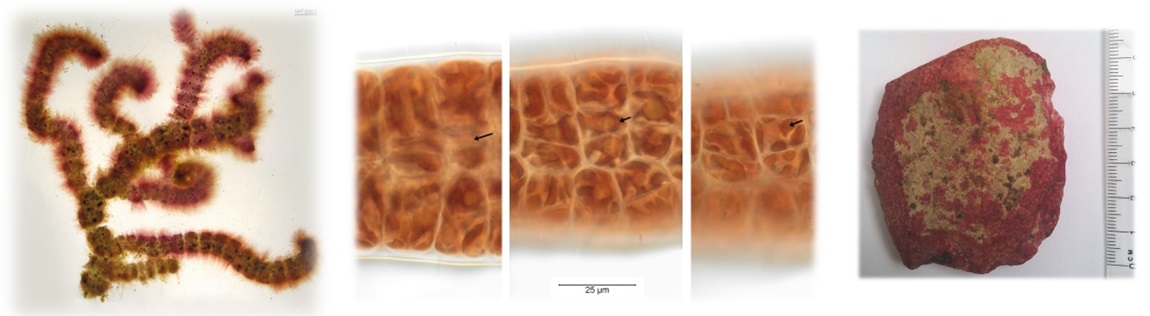
- commonly red due to predominance of phycocyanin and phycoerythrin in chloroplasts
- unicellular, filamentous or pseudoparenchymatous (flagellated stages absent)
- food storage material - various, including floridean starch
- unique features associated with reproduction
Phylum Euglenophyta (euglenoids) - Search Algaevision
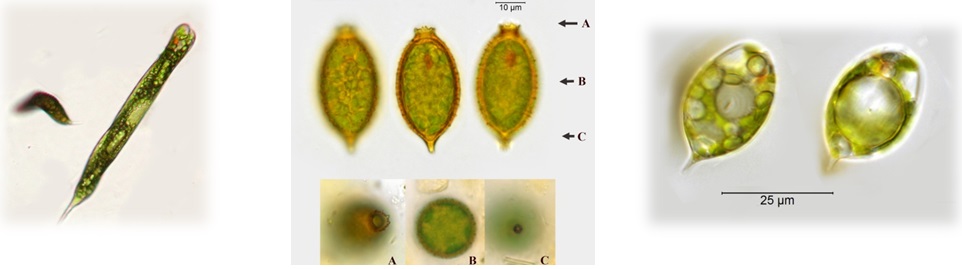
- green
- commonly unicellular
- often exhibit squirming movements, sometimes surrounded by an envelope or lorica
- chloroplasts variously shaped
- one or two flagella arising in a flask-shaped invagination
- eyespot red, usually evident
- walls with longitudinal or spiral striations
- food storage material - paramylon
Phylum Cryptophyta (cryptomonads) - Search Algaevision
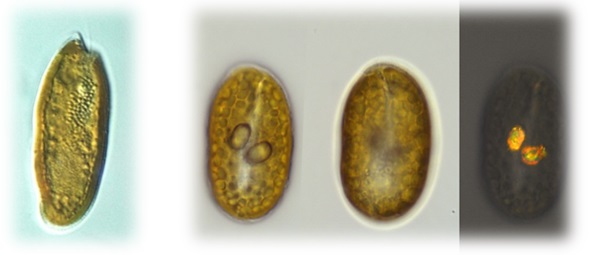
- brown, blue, blue-green, red, red-brown, olive green, or yellow-brown due to accessory
- pigments in one or two chloroplasts
- unicellular (rarely colonial), often bean-shaped, frequently dorsiventrally flattened
- two or more unequal subapical flagella arising in an anterior invagination
- food storage material - starch or starch-like
Phylum Dinophyta (dinoflagellates) - Search Algaevision
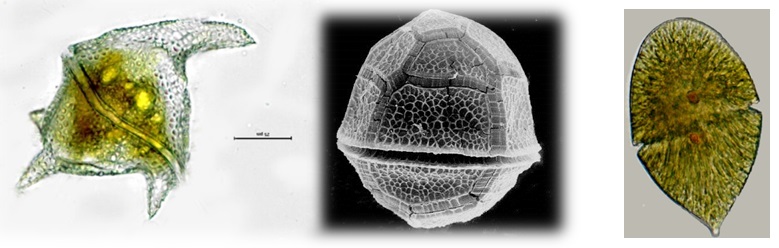
- usually brown due to presence of accessory pigments
- unicellular, rarely coccoid or filamentous
- walls firm or of regularly arranged polygonal plates
- biflagellate - one flagellum transverse and encircling the cell, other directed posteriorly directed
- food storage materials - starch and oil
Phylum Raphidophyta - Search Algaevision
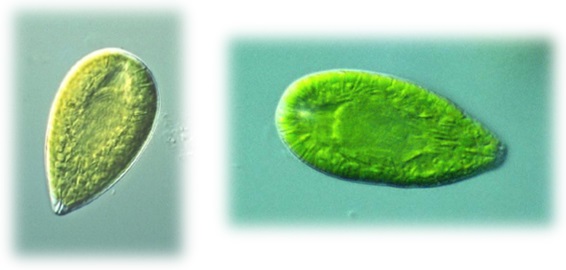
- yellow-green due to predominance of accessory pigment diatoxanthin in two or more chloroplasts
- unicellular, dorsiventrally organised, with no outer wall (naked)
- two flagella arising in an apical, funnel-shaped invagination, one flagellum directed forwards and other backwards
- food storage material - oil
Phylum Haptophyta - Search Algaevision
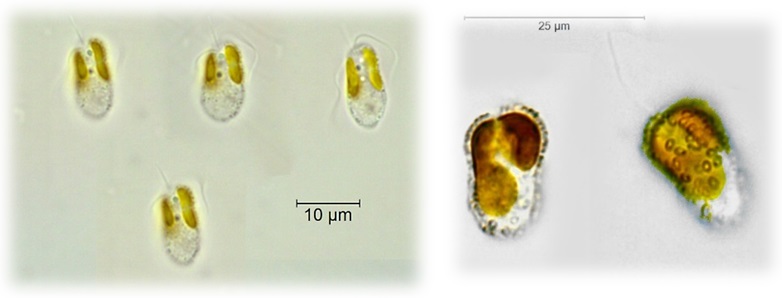
- cells are golden or yellow-brown due to presence of accessory pigments (principally fucoxanthin)
- unicellular
- flagellates have amoeboid, coccoid, palmelloid or filamentous stages
- walls often possess calcified scales
- two flagella, and between them an appendage known as a haptonema
- food storage material - principally chrysolaminarin
Phylum Chrysophyta (golden-brown algae) - Search Algaevision
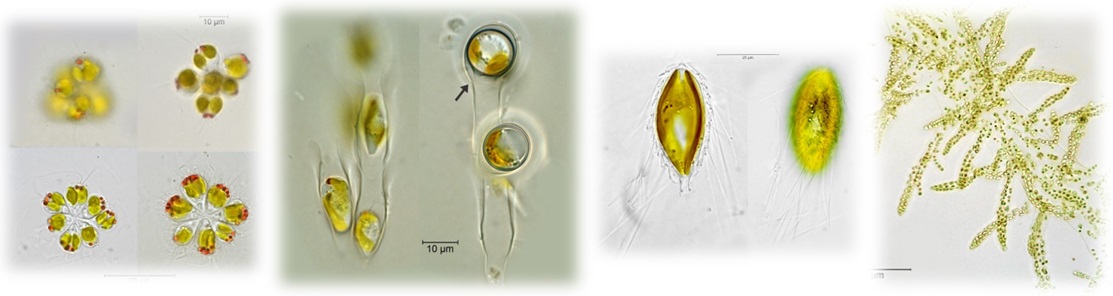
- cells are golden to yellow-brown due to presence of accessory pigments
- single coccoidal cells or palmelloid, filamentous or parenchymatous
- mostly uniflagellate or with two flagella, one long and the other short
- outer wall absent or cell(s) within an often urn-shaped envelope (lorica)
- silica scales sometimes present
- food storage material - oil or leucosin
Phylum Xanthophyta (yellow-green algae) - Search Algaevision

- cells are typically yellow-green due to present of the accessory pigment diatoxanthin in two or more chloroplasts
- unicellular, filamentous, colonial or coenocytic
- motile forms have two subapical flagella
- walls frequently of overlapping parts
- food storage material - oil, fat or leucosin
Phylum Chlorophyta (green algae) - Search Algaevision

- cells with one to several green chloroplasts
- unicellular, colonial, filamentous, coenocytic or macrophytes with robust axes bearing
- worls of branches and branchlets
- motile or non-motile - if motile then normally have one, two or four usually apical flagella
- food storage material - principally starch surrounding in one to several pyrenoids
- sexual reproduction oogamous in some orders
Phylum Eustigmatophyta - Search Algaevision
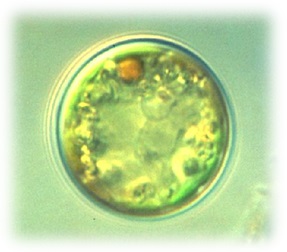
- cells are yellow-green, with main accessory pigment usually violaxanthin in one or more chloroplasts
- unicellular and coccoidal
- motile forms have one flagellum or two unequal flagella inserted near apex
- eyespot unique, independent of chloroplast
- pyrenoid unique
- food storage material unknown
Phylum Phaeophyta (brown algae) - Search Algaevision
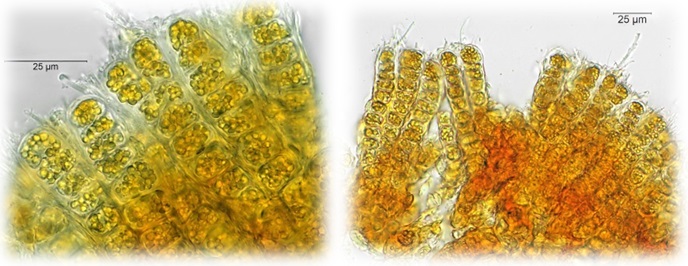
- cells are brownish due to presence of carotenoids pigments (principally fucoxanthin) in one to several chloroplasts
- freshwater species of microscopic branched filaments (often closely packed)
- motile stages pear-shaped with two laterally inserted flagella
- walls frequently contain alginic acid and fucinic acid
- food storage materials - laminarin and mannitol
Phylum Prasinophyta (primitive green algae) - No images currently available on Algaevision
- cells have green, rarely yellow-green, chloroplasts
- unicellular flagellates, rarely non-motile, with one to eight lateral or apical flagella,
- uually arising at base of a depression
- walls and flagella mostly covered with organic scales
- food storage material - starch or mannitol
Phylum Glaucophyta - Search Algaevision
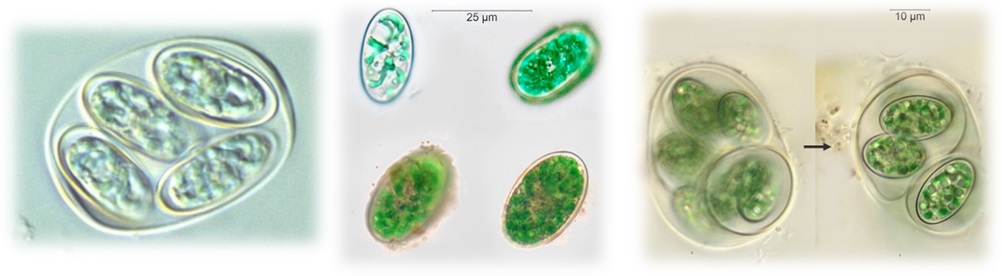
- cells are bright blue-green due to presence of phycocyanin and other pigments in
- cyanelles (not equivalent to chloroplasts)
- unicellular or colonial
- food storage material – starch, produced outside the cyanelles